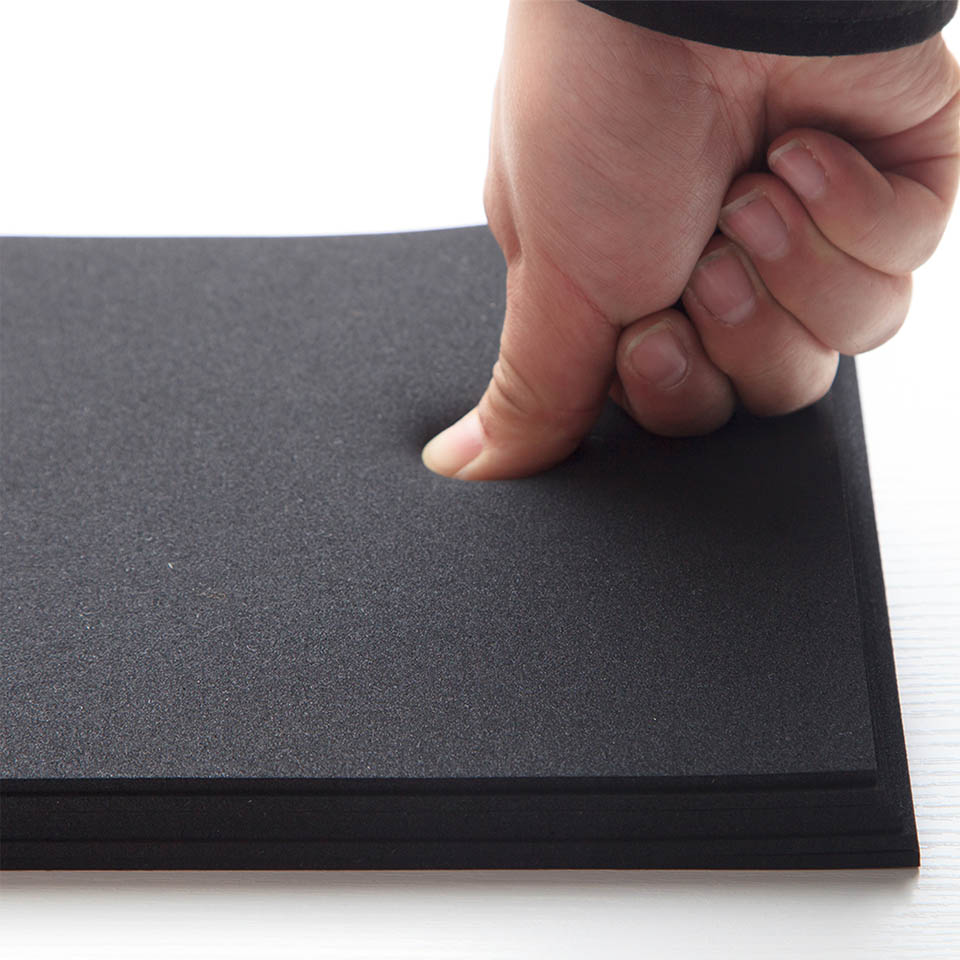
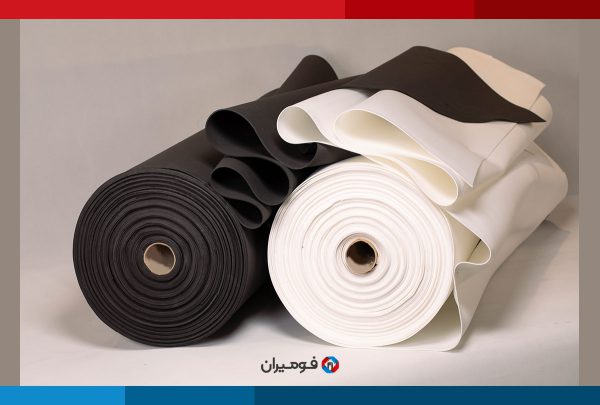
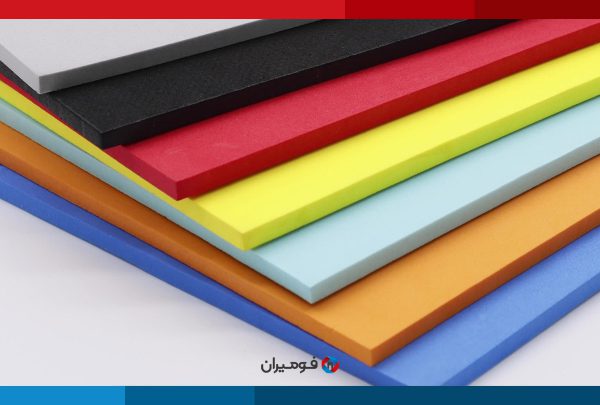
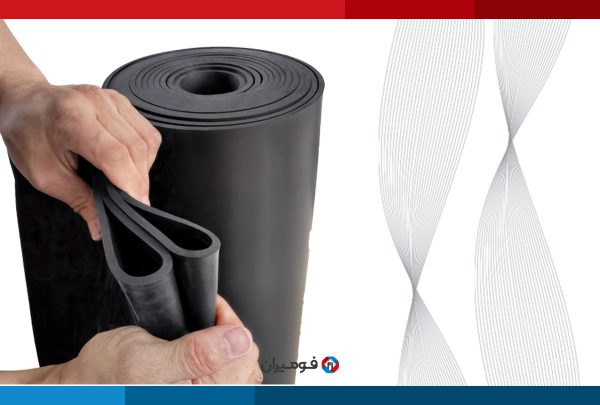
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer foam, otherwise known as EPDM foam, is a synthetic rubber used for a multitude of applications. Its exceptional properties make this rubber ideal for outdoor areas and hot weather. It stands up well to difficult weather, such as hot and cold temperatures, direct sunlight, ozone, alkalinity and acidity, oxygenated solvents, and oxidation. However, it is not compatible with most hydrocarbons, oils, white oil, gasoline, and halogenated solvents. On the other hand, it has great thermal flexibility, and noteworthy resistance to water and steam, which are other important features of EPDM.
EPDM offers compatibility, waterproofing, and excellent insulation. EPDM rubber is used for sealing, making gaskets, and crafting membranes and diaphragms. EPDM is frequently employed when a component requires the ability to restrict fluid passage while still being pliable. It can also be used to provide padding or flexibility. Although EPDM has adequate tensile strength, its pliability makes it inappropriate for rigid items such as cogs, shafts, and structural beams.