Automotive foam refers to specialized foam materials used throughout vehicles for comfort, safety, insulation, and noise control. These foams are engineered to perform in hightemperature environments, resist compression, and improve both the functionality and aesthetic of interior and exterior vehicle components. Their lightweight nature also helps reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, which contributes to better fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. Modern cars include multiple types of foams, such as polyurethane, polyethylene, and expanded polypropylene, each serving a specific purpose.
Automotive foams are used in areas such as seating, headliners, door panels, HVAC ducts, engine insulation, and trunk compartments. They play a crucial role in absorbing impact, damping vibration, sealing gaps, and enhancing acoustic performance. As vehicles become more advanced and customer expectations for comfort and safety rise, the demand for highperformance automotive foam materials continues to grow.
2. Types and Properties of Automotive Foam
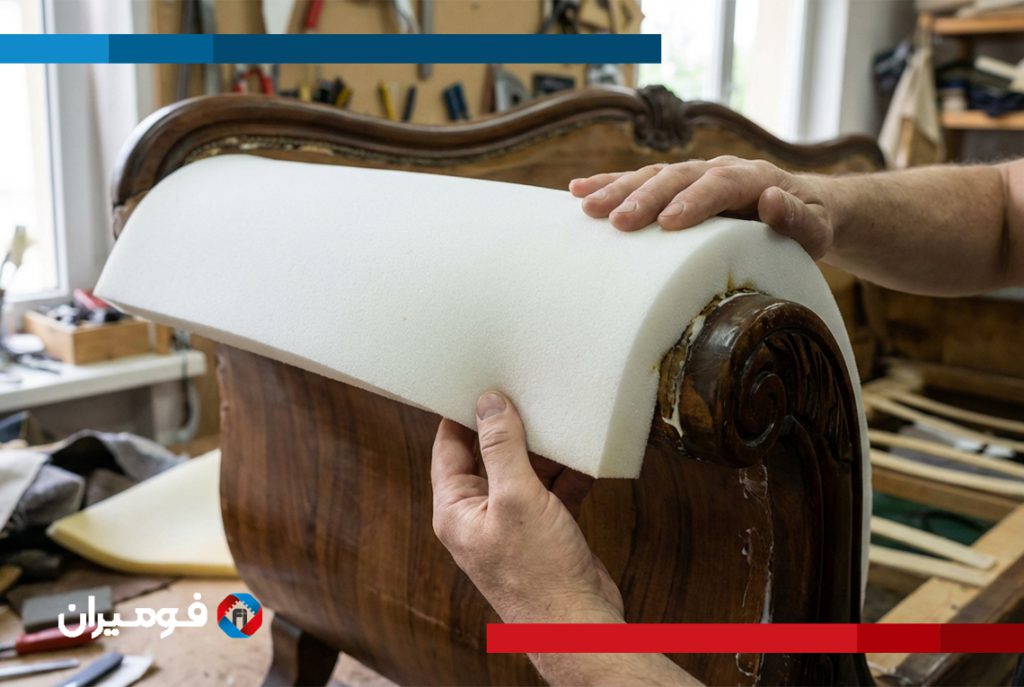
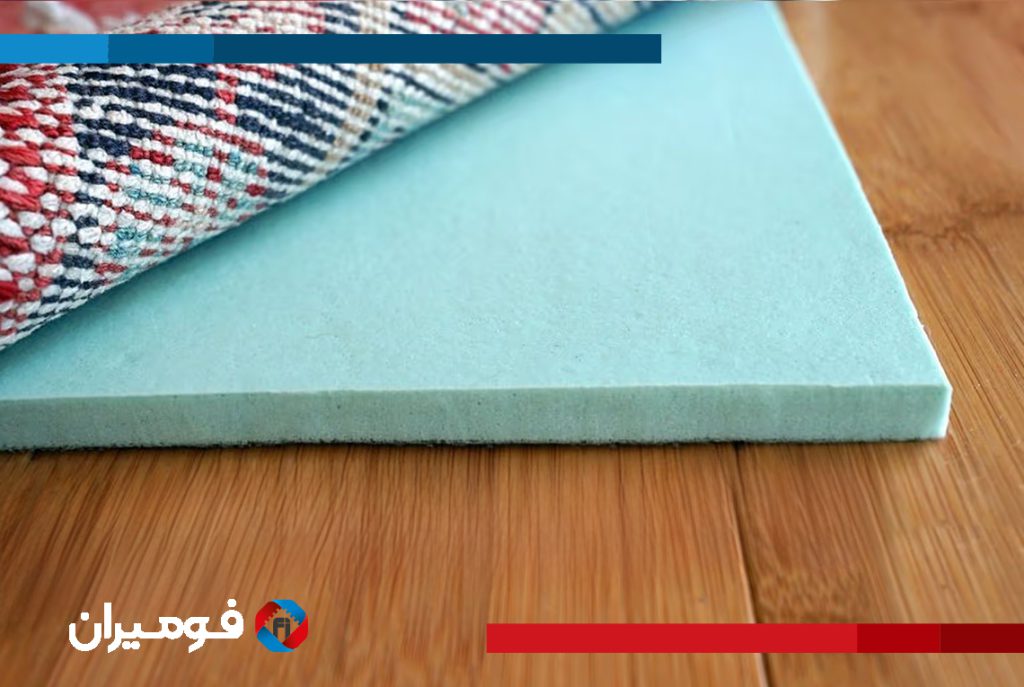
The automotive industry utilizes a range of foam materials depending on the function and performance needs of the component. Polyurethane foam is the most common, known for its cushioning properties and used in car seats and interior padding. Polyethylene foam is valued for its firmness and moisture resistance, ideal for protective panels and insulation. Expanded polypropylene (EPP) and expanded polystyrene (EPS) are used in impact zones due to their excellent energy absorption.
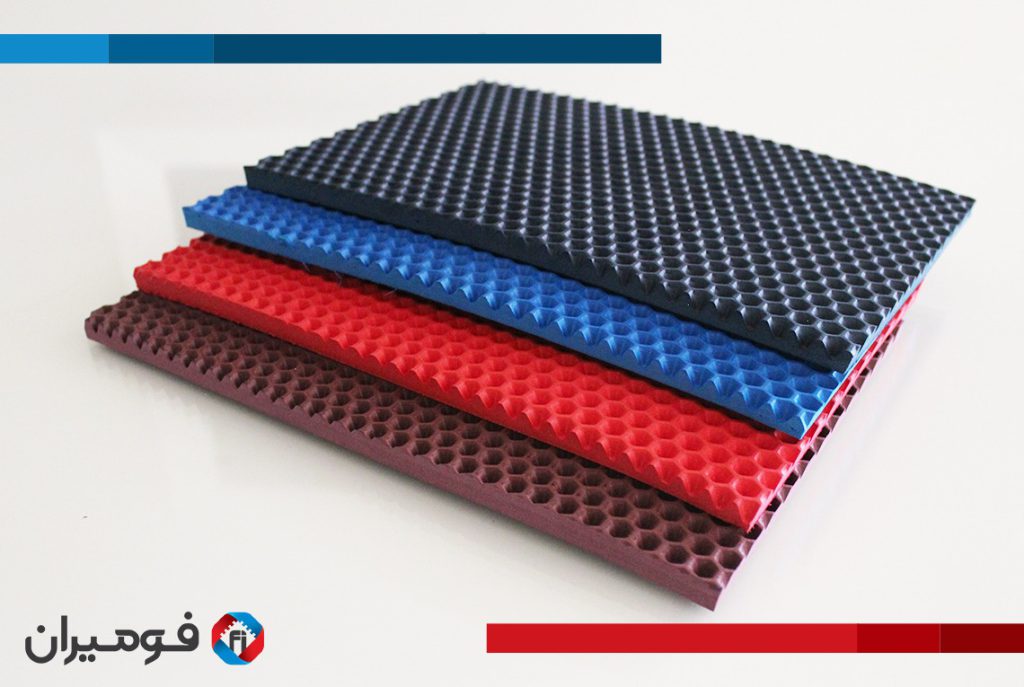
Each foam type is selected based on durability, compression recovery, resistance to heat and chemicals, and environmental exposure. Flame retardancy is a critical property, especially for components used inside the cabin. Closedcell foams are generally more resistant to water and air, making them ideal for sealing and insulation, while opencell foams are better for sound absorption and cushioning.
- Polyurethane Foam
- Polyethylene Foam
- Expanded Polypropylene
- Heat Resistance
- Moisture Barrier
- Cushioning Ability
3. Design and Manufacturing Considerations
Designing automotive foam components requires a balance between comfort, performance, and cost. Foam must be tailored to fit into tight tolerances, especially in layered assemblies like dashboards or HVAC units. Cutting techniques such as diecutting, CNC routing, and waterjet cutting are used to achieve precise shapes. In seat manufacturing, foam is often molded in place to form complex ergonomic contours.
Lamination, adhesive bonding, or mechanical fastening are used to integrate foam with other materials like fabrics, plastics, or metals. Foam parts are also tested for factors like flammability, odor emissions, compressive strength, and thermal resistance to meet industry regulations. As electric vehicles grow in popularity, foam parts are being optimized for battery protection, lightweight body panels, and noise suppression.
- DieCutting
- CNC Routing
- Molded Seats
- Adhesive Bonding
- Thermal Testing
- EV Applications
4. Applications of Automotive Foam
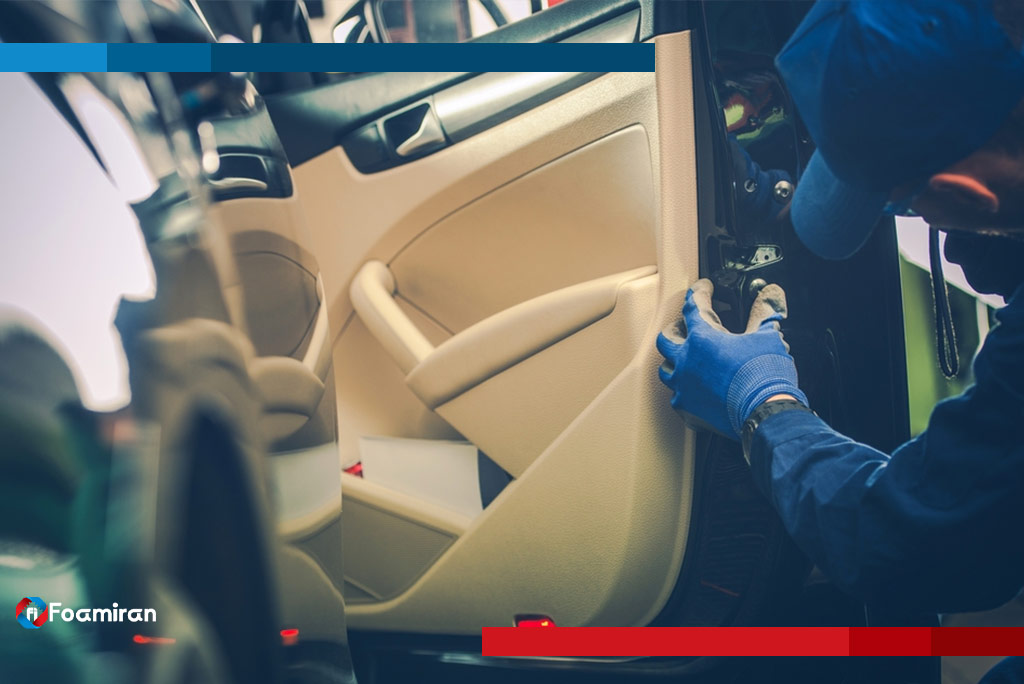
Foam plays an integral role in many parts of a vehicle. In seating systems, it provides ergonomic comfort and shape retention. Headliners and roof insulation use foam to block heat and reduce road noise. Door panels are fitted with foam inserts for both acoustic and structural support. In underhood areas, foams provide thermal and vibration isolation for engine and battery systems.
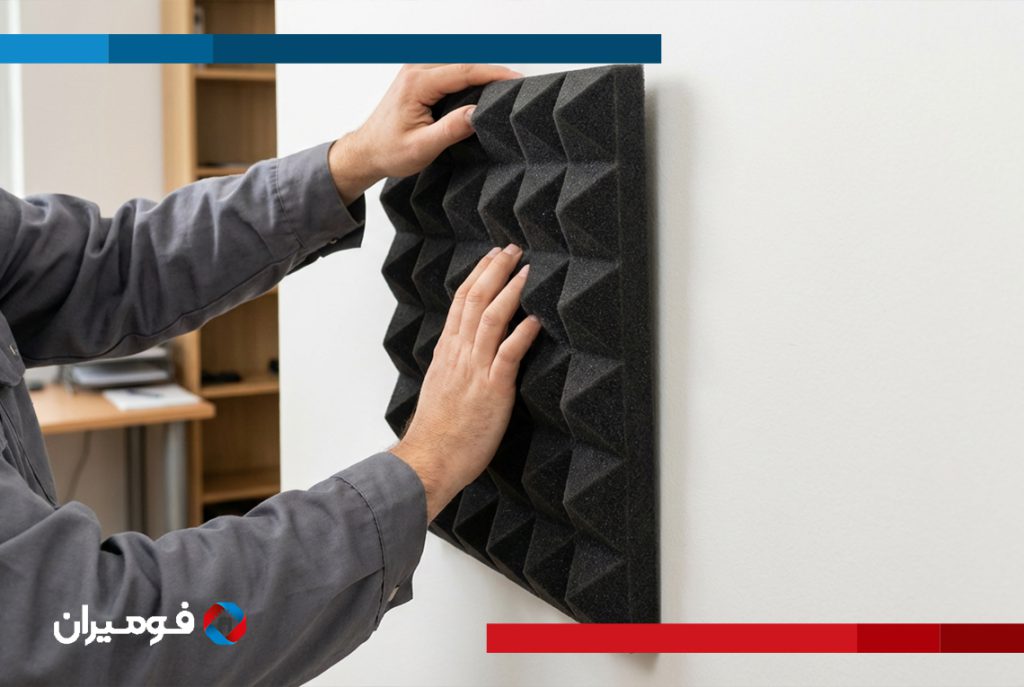
Foam is also widely used in HVAC systems to direct airflow and reduce noise. In trunk compartments, it helps with cushioning and cargo stability. Increasingly, foam is being applied in impact protection zones such as bumpers and headrests, improving passenger safety. Each of these applications leverages the specific characteristics of the foam selected.
- Seats and Cushions
- Headliners
- Door Panels
- Engine Bays
- HVAC Ducts
- Trunk Liners
5. Advantages and Challenges
Automotive foam offers multiple advantages: it is lightweight, costeffective, versatile, and customizable for different automotive parts. Its compressibility allows it to conform to irregular shapes, creating better seals or comfort levels. Foam also enhances vehicle acoustics and thermal insulation, contributing to passenger satisfaction. Moreover, modern foams can be engineered to meet strict flammability and emission standards.
However, there are challenges too. Some foams degrade under prolonged heat or UV exposure. Others may release VOCs (volatile organic compounds), requiring special formulations to meet air quality regulations. Recyclability can also be a concern, especially with multilayered or chemically bonded foams. Manufacturers must carefully balance performance, durability, and environmental impact when selecting foam materials.
- Lightweight Benefit
- Sound Control
- Energy Efficiency
- Heat Sensitivity
- Emission Limits
- Recycling Issues
6. FAQs About Automotive Foam
Q1: What is the most commonly used foam in cars?
A1: Polyurethane foam is the most widely used, especially in seats and interior padding.
Q2: Are automotive foams safe for longterm use?
A2: Yes, they are tested for flammability, VOCs, and durability to meet automotive safety standards.
Q3: Can automotive foam reduce road noise?
A3: Absolutely. Acoustic foams are used in door panels, roofs, and engine bays to absorb noise.
Q4: Is automotive foam used in electric vehicles?
A4: Yes, particularly in battery insulation, lightweight body parts, and noise suppression.