In the world of modern industries, lightweight and efficient materials like foam sheets play a key role in increasing productivity and reducing costs. These materials, with their porous structure, provide excellent insulation and shock absorption, which is ideal for manufacturing industry managers. From construction to packaging, foam sheet guarantees safety and return on investment as an economical solution. In this comprehensive guide, in addition to reviewing types and applications, we also cover history, production process, future trends, and case studies to gain a deeper understanding of this widely used material.
What is a Foam Sheet?
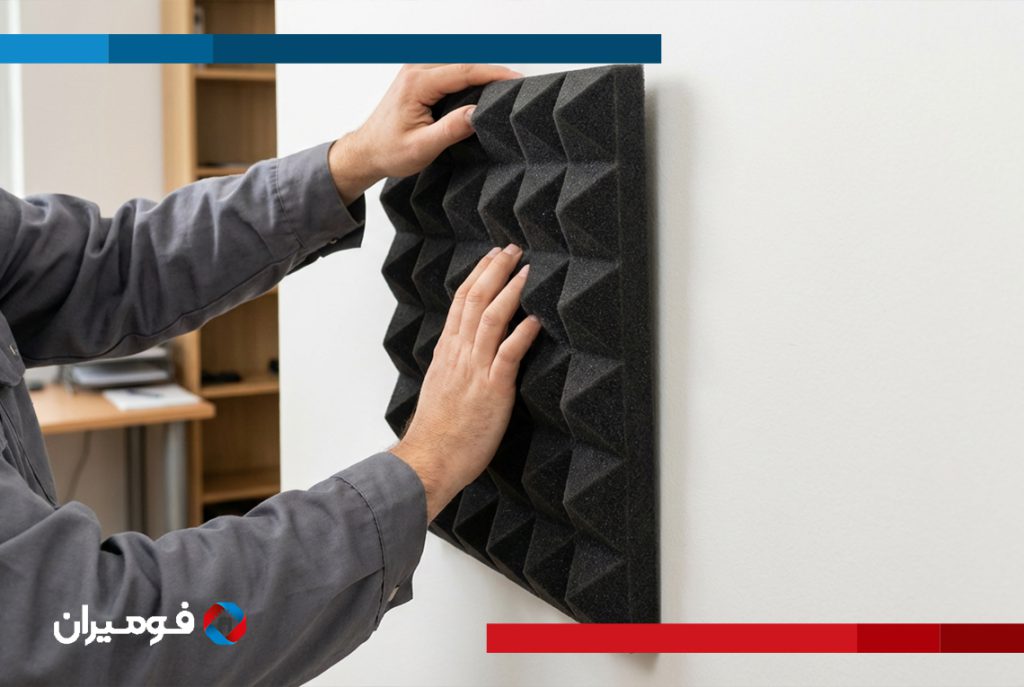
Foam sheet is a polymer material that, through a foaming process, creates a porous structure of small gas-filled cells. This structure reduces weight and increases insulation properties. Based on cell connection, it is divided into two types: closed-cell and open-cell. In the closed-cell type, gas is trapped and creates high impermeability to moisture and heat, which is suitable for humid environments. The open-cell type is more flexible and performs sound and vibration absorption better.
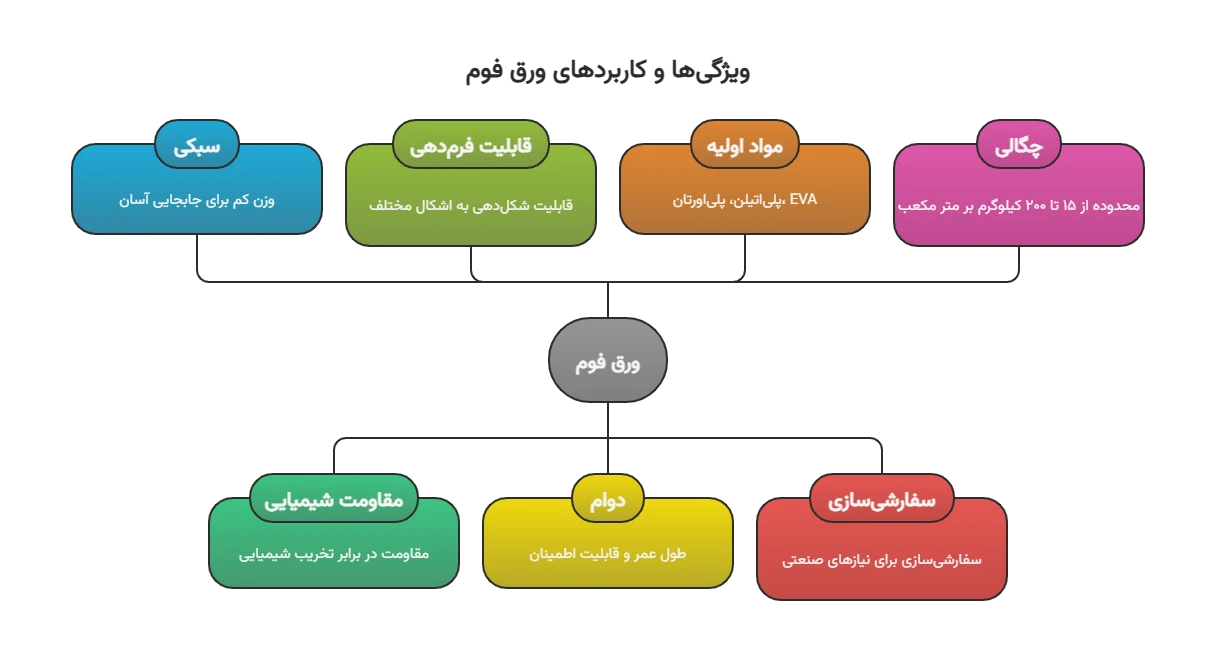
Key features of foam sheets include lightness, chemical resistance, formability, and durability. Raw materials such as polyethylene, polyurethane, and EVA increase diversity. For example, EVA foam sheet with anti-slip properties and UV resistance is prominent in safety-oriented applications.
Foam sheet types can be customized based on industrial needs, which improves return on investment by reducing waste. Additionally, the cellular structure of the foam sheet allows it to be produced in various densities, from 15 to 200 kilograms per cubic meter, making this variety suitable for diverse industries.
History of Foam Sheet: From Discovery to Modern Applications
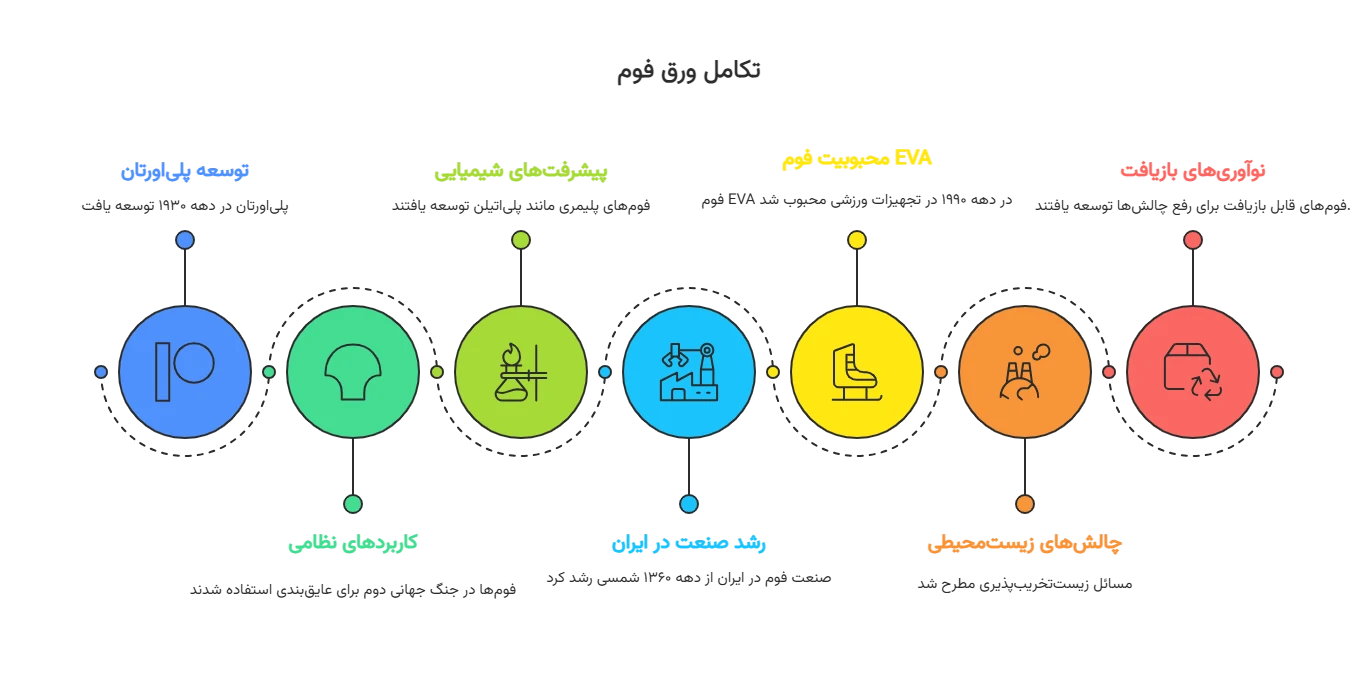
The history of foam sheet dates back to the 1930s, when polyurethane was first developed. This versatile material, with exceptional properties and a wide range of applications, created a major revolution in industries. Initially, foams were used for military applications in World War II, such as aircraft insulation and protective equipment.
In the 1950s, advances in chemical processes led to the production of polymeric foams such as polyethylene and polystyrene, which offered lightness and excellent insulation. Surfactants played a key role in foam stability and made its production easier. In Iran, the foam industry grew from the 1980s, and companies like Foamiran have been engaged in industrial production since 2002.
Today, foam sheet is an integral part of modern industries. For example, in the 1990s, EVA foam became popular in sports equipment due to its high durability. This history indicates the evolution from simple materials to advanced solutions for environmental and industrial challenges.
Over time, challenges such as biodegradability issues were raised, but innovations like recyclable foams have been responsive. Understanding this history helps us better understand the value of foam sheet in the modern supply chain.
Foam Sheet Production Process: From Raw Materials to Final Product
The foam sheet production process involves complex steps starting with the combination of polymeric materials. First, raw materials such as polyethylene or polyurethane are mixed with foaming agents to create a porous structure. In the extrusion method, the mixture is heated and exits through a die to form continuous sheets.
For closed-cell foam, such as EVA, gas is trapped inside the cells to increase impermeability. The process includes foaming, cooling, and cutting stages. In polyurethane foam, isocyanate and polyol are combined and become gel-like, then harden.
The advantages of this process include density and thickness control, which makes customization possible. However, it requires advanced equipment and precise quality control to ensure product durability. In Iran, factories like Foamiran use modern technologies for production with ISO standards.
This process is not only efficient, but with a focus on recyclable materials, it contributes to environmental sustainability. Understanding production details helps industrial managers to optimize the supply chain.
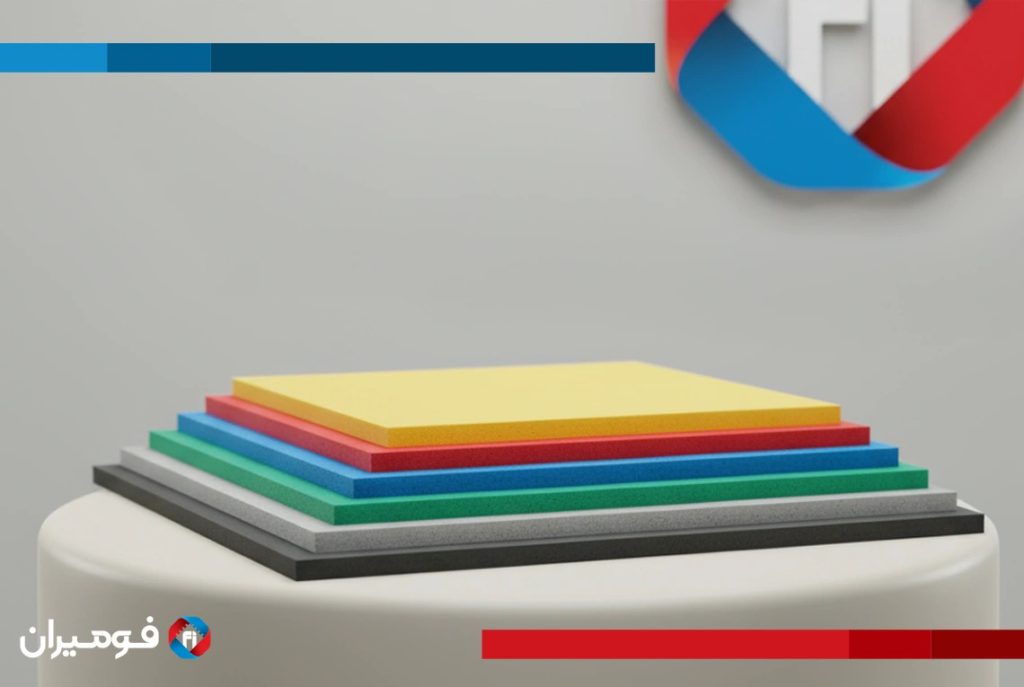
Main Types of Foam Sheet Based on Raw Materials
Foam sheet is produced in various types, each designed for specific applications. Proper selection contributes to the durability and efficiency of the project.
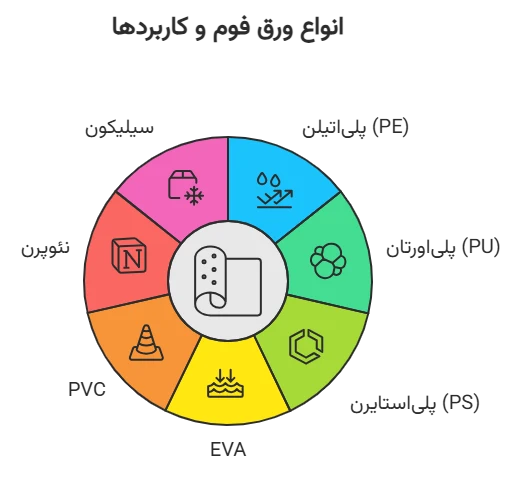
1- Polyethylene (PE): Resistant to moisture and chemicals, suitable for packaging and building insulation.
2- Polyurethane (PU): Soft and flexible, for furniture and filters.
3- Polystyrene (PS or Unolit): Light and thermal insulator, in walls and ceilings.
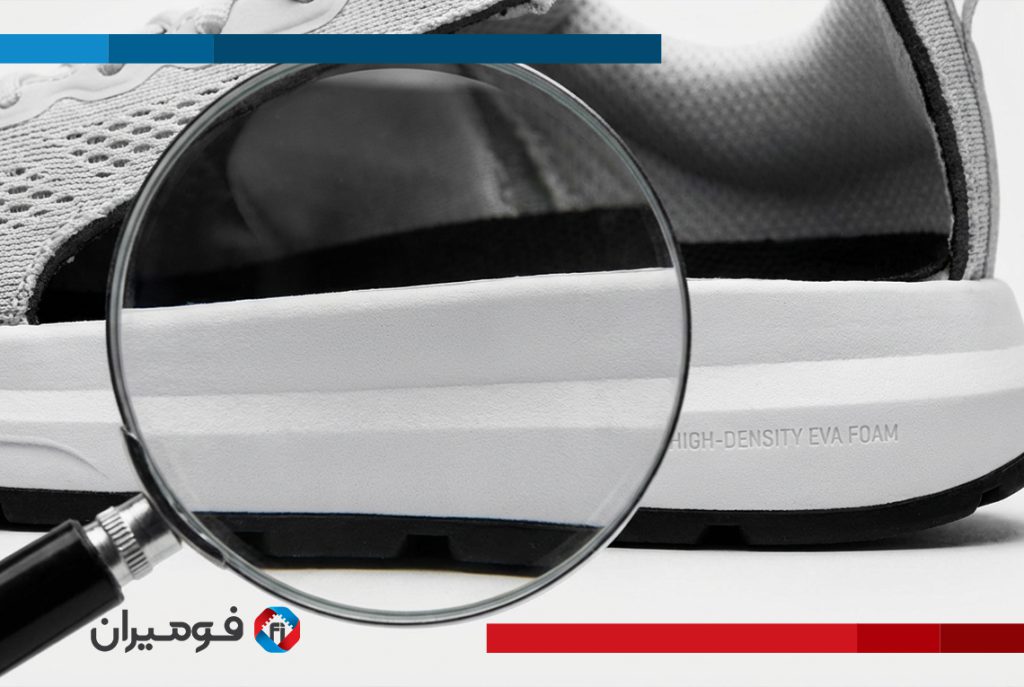
4- EVA: Waterproof, abrasion resistant, for sports flooring and medical equipment.
5- PVC: High durability, for advertising boards.
6- Neoprene: High elasticity, in marine equipment.
7- Silicone: Heat resistant, in pharmaceutical industries.
In addition, specialized types such as latex foam are used for specific applications like mattresses. This variety allows you to choose based on mechanical and environmental needs.
Extensive Applications of Foam Sheet in Various Industries
In packaging, foam sheets absorb shock and prevent damage to sensitive products, which increases return on investment by reducing losses. In construction, as thermal and acoustic insulation, it reduces energy costs by up to 30%.
In the automotive industry, it is used for seats and noise reduction, improving safety. In sports equipment, it creates safe flooring, and in medicine, it makes orthopedic knee braces. Other applications include bags and shoes, textiles, aerospace, and educational toys.
It is also used in the filtration industry, where its open-cell structure facilitates absorption and filtration. Additionally, in food and pharmaceutical industries, silicone foam is used due to its high thermal resistance.
Case Studies: Real Applications of Foam Sheet
In a case study from the automotive industry, the use of PU foam sheets in seats led to a 20% weight reduction and increased comfort. In construction, a project in Iran using XPS foam reduced energy consumption by 25%.
In medical equipment, EVA foam sheet in the production of prosthetics increased durability and safety. These examples indicate the real impact of foam sheet on improving performance and reducing costs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Foam Sheet
Advantages of foam sheets include lightness for easy transport, insulation for energy saving, and moisture resistance for harsh environments. High durability and recyclability make it eco-friendly. Flexibility allows for customization, which is ideal for B2B projects.
Disadvantages: Limited compressive strength in soft types, temperature limitations, and UV sensitivity in some cases. With proper selection, such as resistant EVA, these issues are mitigated (Wikipedia Foam).
Overall, the advantages outweigh the disadvantages, especially in industrial applications where safety and efficiency are priorities. Additionally, high-density foams like rubber foam have high chemical resistance.
Difference Between Foam Sheet and Foam Roll
Foam sheet is flat and in fixed dimensions, suitable for precise cutting. Foam roll is flexible for large coverage.
– Roll selection: For extensive surfaces like flooring.
– Sheet selection: For specific shaping like decoration.
– Roll for quick installation in buildings.
– Sheet for precise insulation.
– Roll has a higher return on investment in large areas.
– Sheet for custom projects with greater safety.
Additionally, foam roll is often used for longitudinal applications like piping, while sheet is more suitable for building panels.
Comparison of Foam Sheet with Alternative Materials
Compared to traditional materials like wood or metal, foam sheet has lower weight and cost. For example, in insulation, XPS foam offers higher moisture resistance compared to glass wool. However, in high-pressure environments, it may need to be combined with harder materials.
This comparison helps to make the optimal choice based on budget and project needs.
Future Trends and Innovations in Foam Sheet
The future of foam sheet is bright with a focus on sustainability, such as biodegradable foams. Innovations like nano foams for better insulation are being developed. In Iran, companies like Foamiran are investing in exports and green technologies.
These trends will turn foam sheet into a key material in the green economy.
Care, Maintenance, and Safety Tips
For maintenance, keep the foam sheet in a dry place away from the sun. Cleaning should be done with mild detergent. Safety: Proper ventilation during cutting, avoiding heat.
Observing these points extends the life of the foam sheet and reduces safety risks. Additionally, in chemical environments, use resistant foams.
Foamiran: Leader in Foam Sheet Production in Iran
Foamiran started work in 2002 with an area of 8500 square meters and expanded in phases in 2003 and 2014. With ISO 9001, 14001, 45001, Nano, and IMS certificates, it is the largest manufacturer in Iran and the Middle East. It offers EVA exports and cutting, lamination, molding, and adhesive services for customization.