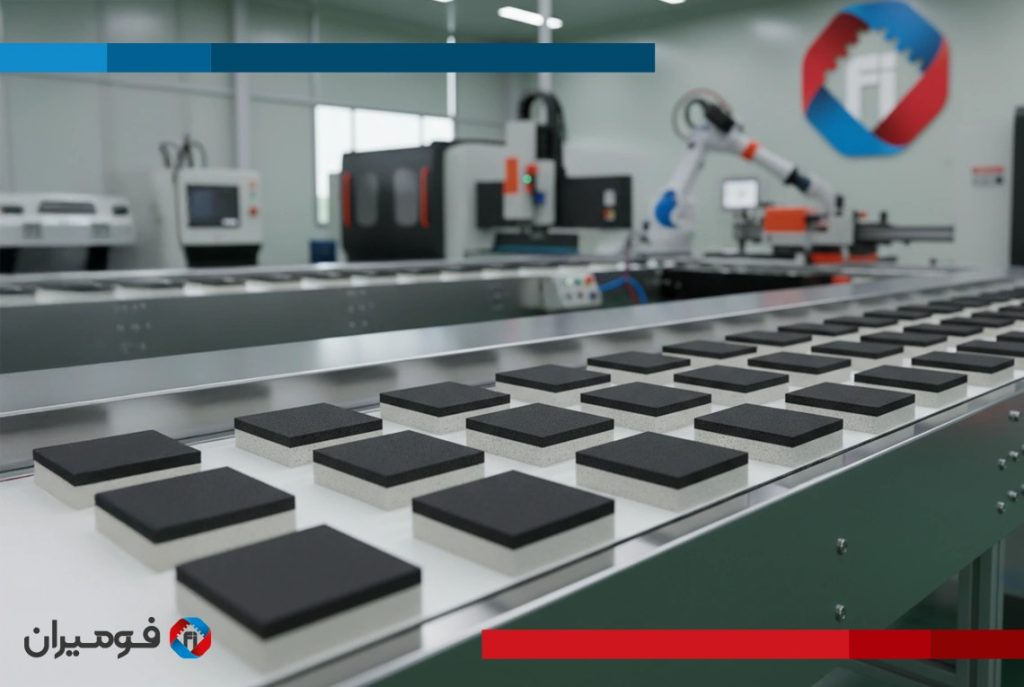
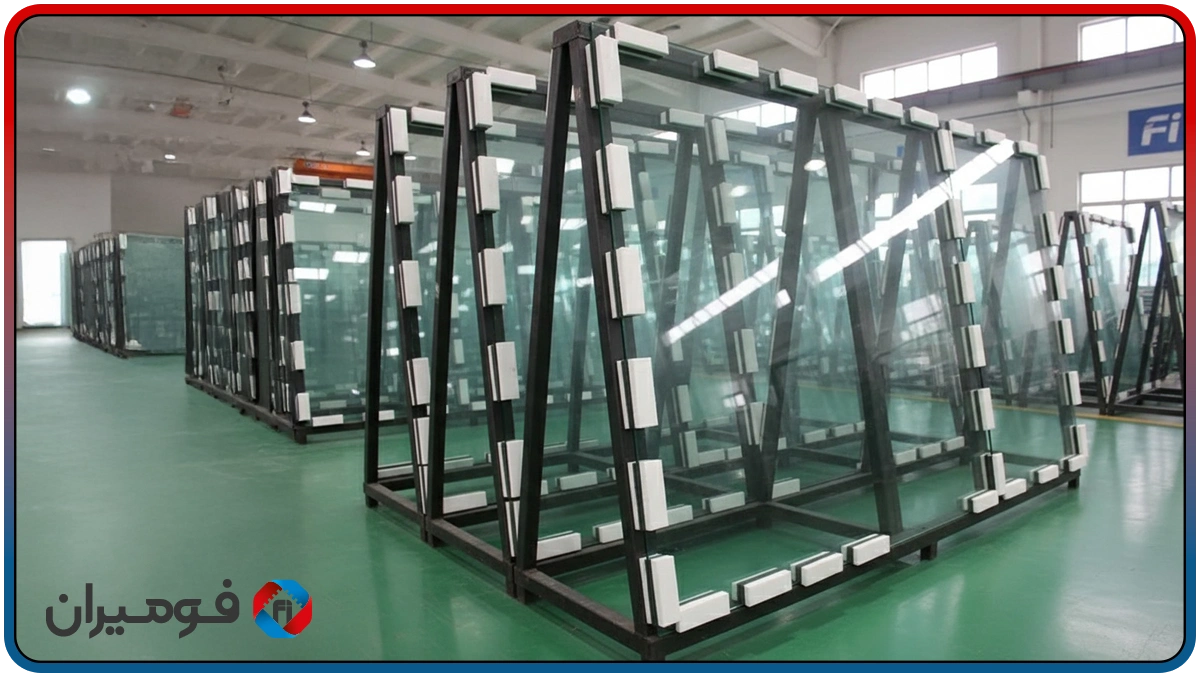
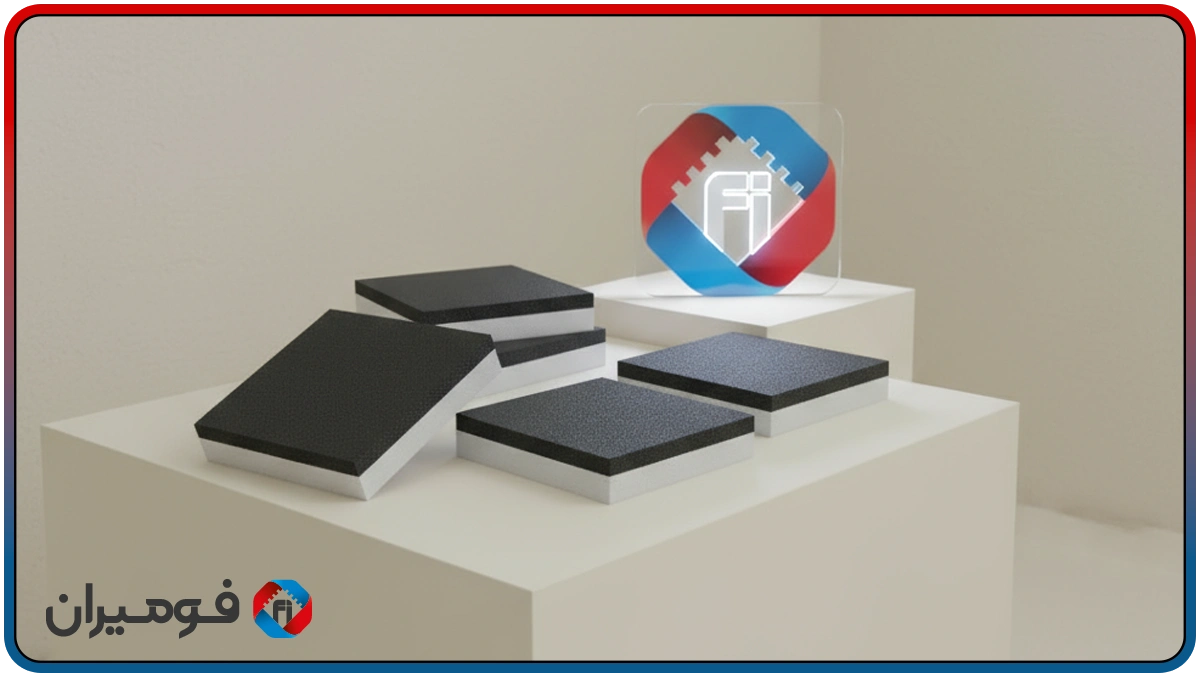
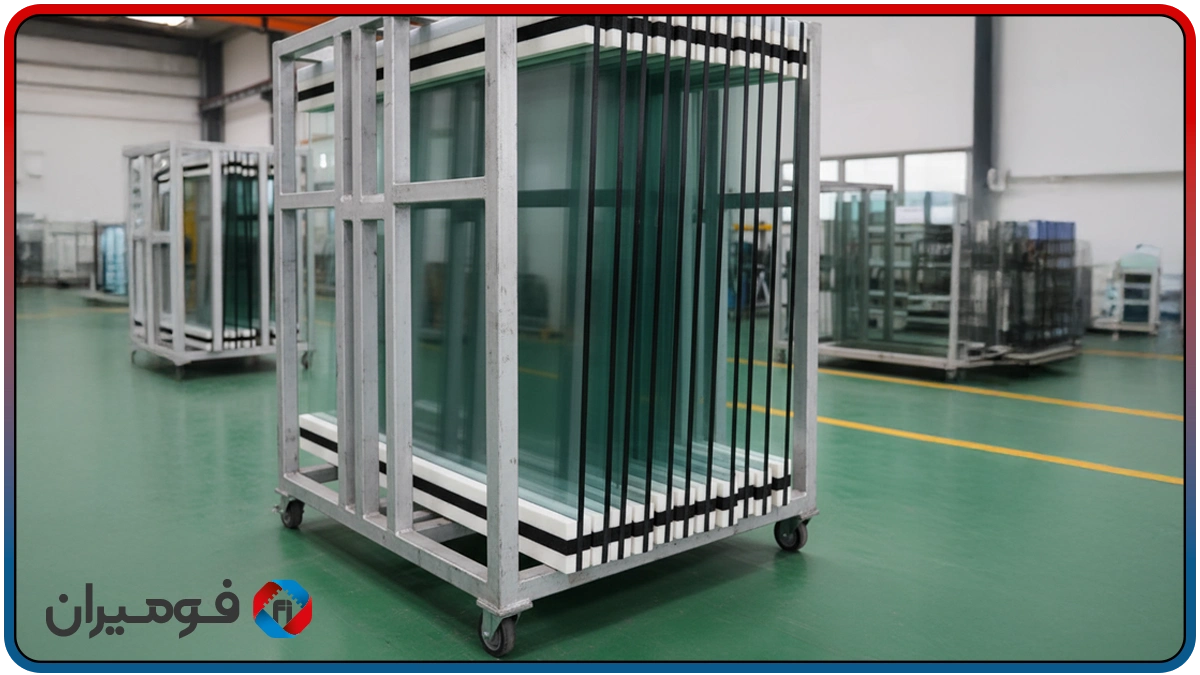
Tempered glass transport foam pads for the safe transport of tempered/laminated glass in various racks and chassis, the combination of a “structural compressed foam core (EVA/PE)” and a “T-damping layer” is a lightweight, durable, and moisture-resistant solution. The total pad thickness is usually selected between 8 and 20 mm (4–10 mm compressed core + 4–10 mm T-layer), and as glass dimensions/weight increase, density and thickness are engineered to increase. Impact behavior tests on tempered glass have shown that point impacts and repetitive vibrations can lead to micro-cracks and sudden breakage; therefore, the presence of a uniform contact layer and effective damping during transport is vital.
Why Does Tempered Glass Need Specialized Foam Protection?
Tempered glass is resistant in terms of general bending load, but remains vulnerable to point impacts and repetitive vibrations. In the transport process, every bump or braking action can create concentrated stresses; if the contact layer is not soft and uniform, edges and corners face the highest risk of breakage. For this reason, using a system that provides both a “rigid structure” for stress distribution and “actual shock absorption” is a logical choice.
Package Anatomy: Structural Core + Damping Layer (and Optional Coating)
The pad core is a closed-cell foam with higher density that provides dimensional stability and prevents local bending; the damping layer is a softer foam with rapid resilience that dampens instantaneous shocks and transport route vibrations. If needed, a laminated felt/fabric coating (adhesive-backed) can be added for controlled friction and scratch prevention. The closed-cell nature of both layers practically eliminates water penetration and keeps maintenance simple.
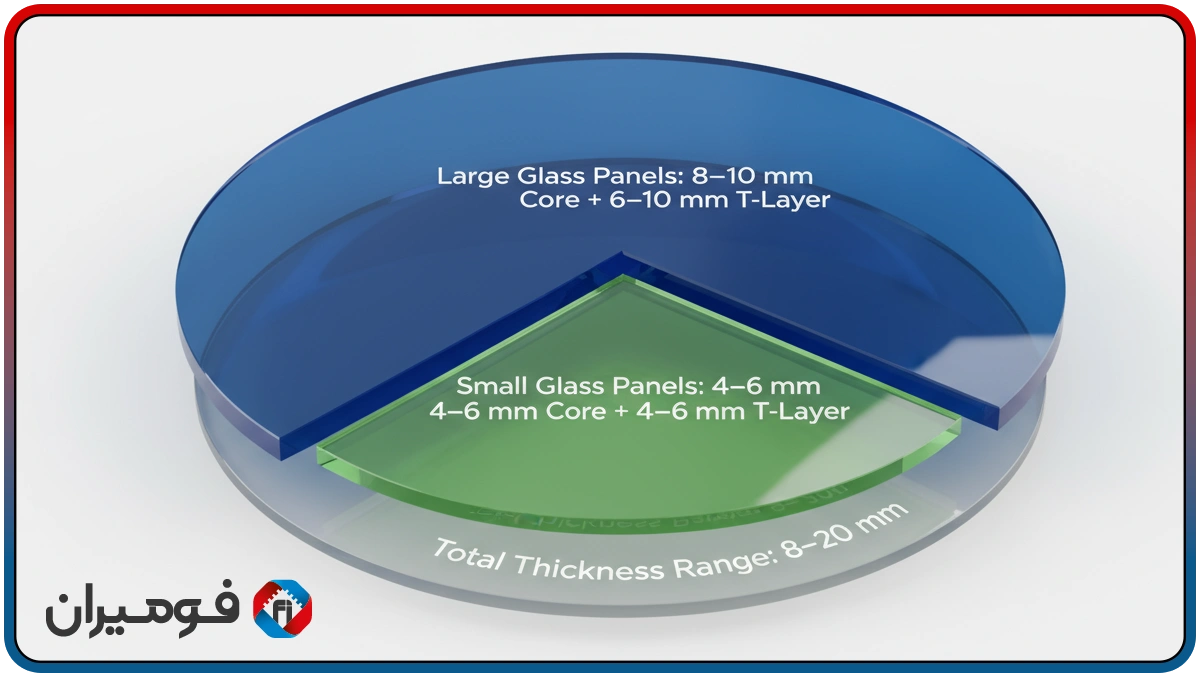
Selection of Thickness and Hardness Based on Weight and Dimensions
The rule is simple: the greater the dimensions and weight of the glass, the more we need a “denser core” and/or “higher total thickness” so that local settling is minimized and impact accelerations are dampened. The suggested total thickness range is 8 to 20 mm, which is usually formed from a combination of 4–10 mm compressed core and 4–10 mm T-layer. For small glasses up to a width of ~1.5 meters, 4–6 mm core + 4–6 mm T-layer is sufficient; for larger dimensions/weights, 8–10 mm core + 6–10 mm T is recommended.
Recommended Materials for Each Layer
In the damping layer, T-Foam Sheet is used; controlled softness, high resilience, and closed-cell structure provide reliable shock absorption and vibration damping (NVH). In the structural layer, Compressed Foam (EVA/PE blend) with higher density and hardness guarantees stress distribution and dimensional stability, preventing local settling under glass edges. This combination offers an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, water impermeability, and high durability in high-traffic lines.
Manufacturing Process and Installation Method of Glass Transport Foam Pads
At Foamiran, the production process of glass protection foam pads is designed to maintain both speed and precision. For high-volume production, Die-cutting machines are used, which enable uniform, fast, and precise cutting. When parts have complex forms or specific dimensions, cutting is done via CNC or Waterjet so that edges remain perfectly clean and without thermal distortion. This cutting precision ensures that pads fit perfectly onto transport racks and chassis and do not deform over time.
In the installation stage, depending on the application type and environmental conditions, several different methods are employed. The simplest and fastest method is using industrial adhesive backing, which minimizes installation time, especially in assembly lines or high-traffic projects. For metal structures or heavy racks where mechanical durability is of higher importance, installation with screws and threads along with wide washers is recommended to guarantee pad adhesion and strength against vibration and impact. Also, if quick replacement or temporary installation is needed, slot systems or removable brackets can be used. This flexibility in design and installation makes Foamiran tempered glass transport foam pads easily compatible with various industrial chassis and racks, ensuring the best possible durability and safety in glass transport.
Technical Specification Table of Tempered Glass Transport Foam Pads
Testing and Quality Control
To ensure performance, compression/resilience tests, three-point bending, and Drop/Shock tests on a reference glass sample are recommended. If the acceleration peak is high, correction is made by increasing core density or T-layer thickness. Temperature/humidity cycles also confirm performance stability due to the closed-cell nature. The tempered glass transport foam pad plays an effective role in its transport security.
Why Is Foamiran the Reliable Choice for Designing and Producing Specialized Foam Pads?
Foamiran, with over two decades of experience in the Iranian foam industry, is considered one of the leading manufacturers of engineering foams in the Middle East. Relying on R&D capabilities, materials engineering, and production lines equipped with Die-cutting, CNC, and Waterjet technologies, this group is capable of designing and producing any type of foam pad or bumper (tempered glass transport foam pad) from the idea stage to mass production. By continuously collaborating with construction, glass, automotive, and packaging industries, Foamiran offers precise solutions for protection, sealing, and shock absorption to guarantee the quality and durability of the final product.
All design and production processes at Foamiran are carried out in accordance with the requirements of international management systems ISO 9001:2015 (Quality), ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety). This compliance guarantees complete quality control at all stages of production from raw materials to packaging. Foamiran’s two flagship products in the glass transport sector, namely Compressed Foam Sheet for stress distribution and dimensional stability and T-Foam Sheet for shock absorption and vibration damping, are examples of the combination of Foamiran’s engineering knowledge and production precision, which have been successfully used in major industrial projects.