EPDM foam order
What is EPDM?
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer foam, otherwise known as EPDM foam, is a synthetic rubber used for a multitude of applications. Its exceptional properties make this rubber ideal for outdoor areas and hot weather. It stands up well to difficult weather, such as hot and cold temperatures, direct sunlight, ozone, alkalinity and acidity, oxygenated solvents, and oxidation. However, it is not compatible with most hydrocarbons, oils, white oil, gasoline, and halogenated solvents. On the other hand, it has great thermal flexibility, and noteworthy resistance to water and steam, which are other important features of EPDM.
EPDM offers compatibility, waterproofing, and excellent insulation. EPDM rubber is used for sealing, making gaskets, and crafting membranes and diaphragms. EPDM is frequently employed when a component requires the ability to restrict fluid passage while still being pliable. It can also be used to provide padding or flexibility. Although EPDM has adequate tensile strength, its pliability makes it inappropriate for rigid items such as cogs, shafts, and structural beams.
EPDM stands for “Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer,” which is used in various industries due to its unique characteristics. Each EPDM product will have its distinctive features, depending on the intended purpose for which it is manufactured. To download the EPDM foam datasheet, please click on the following link:
The characteristics of EPDM foam
The chemical composition of EPDM has created a very durable material with a long lifespan compared to other materials. In addition, EPDM foam is a closed-cell foam. One of the key features of closed-cell materials is the unique structure of the material, which prevents the growth of bacteria and molds. he does.
- High tear resistance
- Medium density
- Elongation to moderate tearing
- High resistance to UV and ozone
- High flexibility and reversibility
- Moderate resistance to direct heat
- Waterproof, sound insulation, heat and cold
- Usable temperature range -40 to +105 degrees Celsius
EPDM Applications
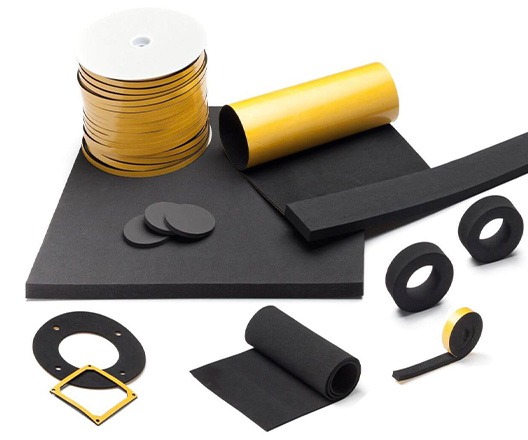
EPDM foam stands out from other materials due to its superior properties and quality, making it a desirable choice for a range of applications and sectors. EPDM is a highly rated material that is suitable for a wide range of uses and is extensively used in the automotive industry for various vehicle components. Its outstanding strength and other advantageous qualities make EPDM foam the perfect material for automotive use. It is mainly used for sealing up windows and doors, reducing vibration, providing better insulation, and making hoses and washers.
EPDM foam has proven to be very resistant to UV radiation, ozone, alkaline substances, water, heat, steam, and weather conditions; however, it has been found to have lesser resistance to some oil-based products. Some of these substances include grease, petroleum derivatives, hot tar, and vegetable and mineral oils, which should be avoided.
- Aerospace industry
- Construction industry (door and window sealant, etc.)
- Automotive industry (types of washers, door and window sealants, vibration reduction and insulation, etc.)
- Railway and subway
- All kinds of industrial washers (for sealing and insulation)
- Shipbuilding industry (insulation of ship hull, types of washers, etc.)
EPDM foam products
Technical Data
| Product code | Sheet dimensions (cm) | Sheet layer dimensions (cm) | Foam roll dimensions | Foam hardness | Foam density (kg/cm3) | Temperature range | Physical characteristics | Colors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM200 | 170*110*28 100*150*24 | 170*110 100*150 | - | 5-15 / Shore C | 200±5 | 40- to105°C | Elastic foam | مشکی |
| EPDM420 | 210*110*35 | 210*110 | 50m*150cm 50m*120cm 100m*150cm 100m*120cm | 105±5 | EPDM | مشکی | ||
| EPDM550 | 240*140*35 | 240*140 | 135±5 | EPDM | مشکی |
Services
| Product Code | Embossing | Thermal laminate | Towel | Punch | Thermoforming | Class welding | Die Cut | CNC | Glitter | Gum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM200 | * | * | * | * | * | * | ||||
| EPDM420 | * | * | * | * | * | * | ||||
| EPDM550 | * | * | * | * | * | * |
Frequently Asked Questions
Is buying EPDM foam only in bulk?
Yes- we have wholesale buying and selling for all our products at Foamiran. You can have a free pre-purchase consultation with our experts for more information about EPDM materials. State your needs so that the most suitable foam will be introduced to you.
How to send EPDM foam for sale outside of Iran?
Foamiran export team has valuable experience in this field. We are ready to give you any guidance and advice to export EPDM foam or any other product. Be in touch with us.
Where are EPDM foams used the most?
The automotive industry is one of the main customers of EPDM foam. Packaging, logistics, construction, aerospace, shipbuilding, insulation, etc. This foam is very resistant to environmental conditions.